Vitamin C: A Brief History
Also known as ascorbic acid or L-ascorbic acid, vitamin C was only discovered in the 1930s by a Hungarian-born researcher named Albert Szent-Györgyi. But long before vitamin C was identified as a specific chemical substance, doctors and scientists had realised that citrus fruits (a key source of the vitamin) had certain health benefits.
Sailors on long voyages, with limited food provisions, would often suffer from scurvy – a painful condition with symptoms such as swollen joints and bleeding gums. However, it was found that giving each sailor rations of citrus fruit or juice could prevent scurvy, though it was only with the later discovery of vitamin C that scientists realised what the “magic ingredient” in the fruit actually was.
What Does Vitamin C Do in Your Body?
We now know that the reason those sailors benefitted from their lemon rations was that the vitamin C they received helped to keep their bodies fit and healthy in numerous ways. Let’s take a look at some of the health-building properties of vitamin C:
Cell Protection: Vitamin C is an antioxidant, meaning that it protects your cells from damage by harmful substances called free radicals. The vitamin binds with and neutralises the free radicals, preventing them from damaging the tissues in your body.
Collagen Production: Collagen is the body’s major building protein that is essential for your internal organs and connective tissues to function properly. Vitamin C helps to ensure that the body keeps producing enough collagen to maintain healthy skin, bones, and blood vessels.
Immune System: Vitamin C works to boost your immunity and help your body fight off infection. Although, as is sometimes thought, it can’t prevent you catching a cold, studies suggest that vitamin C can reduce the duration of cold symptoms.
Wound Healing: If you injure yourself then vitamin C plays a role in your recovery and the swift healing of any wounds.
Iron Absorption: Following a vegetarian or vegan diet? You may be interested to know that vitamin C helps the body to absorb non-haem iron – that is, iron from plant sources, which is usually more difficult for the body to use. This can prevent iron-deficiency anaemia.

How Much Vitamin C Per Day is Best?
According to NIH, the recommended allowance of vitamin C ranges between 15mg and 75mg for children, 90mg for adult men and 75mg for adult women. Women who are pregnant or lactating should consume more – up to 120mg per day. Smokers need an extra 35mg per day.
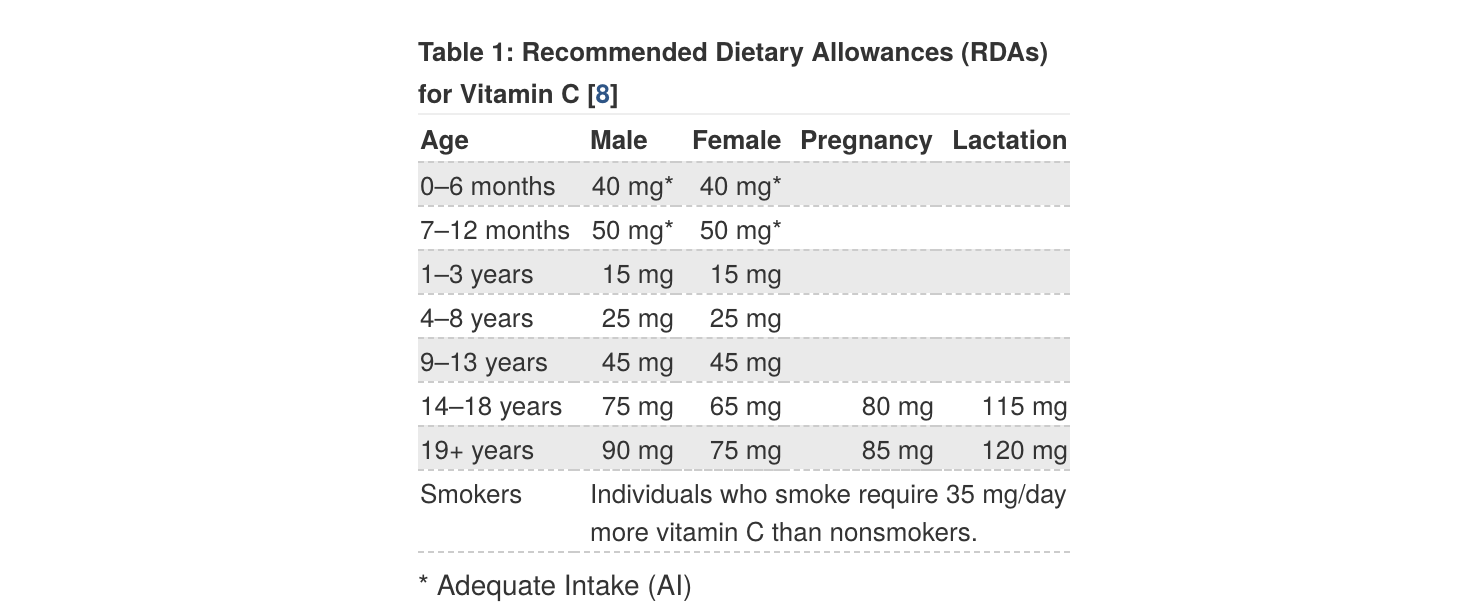
Image source: NIH fact sheet for professionals
Usually you can get enough vitamin C from a varied diet that includes lots of fruit and veg (see below) but you can also take a supplement. Most multivitamin supplements contain vitamin C, or alternatively you can take it on its own.
When you look at the label on the supplement, you may see the vitamin listed as “ascorbic acid”, “ascorbic acid with bioflavonoids”, or “sodium ascorbate”. A supplement that contains ascorbic acid is a good choice, as this is a form of vitamin C that is easier for the body to absorb.
While serious vitamin C deficiency (leading to scurvy) is now rare, certain health conditions make deficiency more likely. These include AIDS, cancer, and tuberculosis.
Which Foods Are Best For Vitamin C?
Most fruits and vegetables contain some vitamin C; however, certain varieties are particularly valuable sources of the nutrient. These are:
Vegetables: Peppers, tomatoes, potatoes (particularly new potatoes), and green vegetables such as broccoli and brussels sprouts.
Fruit: Oranges and orange juice, other citrus fruits, strawberries, and blackcurrants.
It’s important to be aware that processing and/or cooking can reduce or destroy the vitamin C in a food. Boiling vegetables is especially harmful. So try light cooking (such as steaming) and eating some of your fruit and veg raw for optimum vitamin C levels.
Can You Have Too Much Vitamin C?
The reason we need to top up our vitamin C regularly is that the nutrient is water soluble: in other words, our bodies can’t store it and it gets flushed out when you urinate.
Because of this, it’s quite difficult to have too much vitamin C in your diet – even with lots of fruit and veg and a moderate supplement. Potential problems usually only arise when you’re taking very high vitamin C supplements of more than 1,000mg every day. This can cause stomach pain, diarrhoea, and flatulence.
You should also be careful if you suffer from haemochromatosis, a condition where your body retains too much iron in your blood. That’s because (as we saw above) vitamin C can increase iron absorption.
Key Takeaways…
Getting enough vitamin C is crucial if you want to stay fit and healthy. Reaching the recommended amount per day is easy with a diet that features plenty of fruit and veg, and for an extra boost you can always try a vitamin C supplement.
While we've ensured that everything you read on the Health Centre is medically reviewed and approved, information presented here is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. It should never be relied upon for specific medical advice. If you have any questions or concerns, please talk to your doctor.




